# download the happiness data
download.file(url = "https://github.com/jcooperstone/dataviz-site/raw/refs/heads/master/2_04_wrangling/data/hapiscore_whr.csv",
destfile = "happiness.csv")Using Copilot, chattr, and ellmer

chattr and ellmer hexes1 Introduction
We have spent the last handful of sessions using GitHub Copilot embedded in the RStudio IDE. Today we are going to try using:
1.1 Loading data
Let’s use the same data as last week to play around. If you have it from last week, no need to download, but if you need to get it, you can download the file using the code below.
Remember that files with by default be downloaded into your working directory.
And some data on life expectancy around the world from 1800 to predicted values from 2022-2100.
# download the life expectancy data
download.file(url = "https://github.com/jcooperstone/dataviz-site/raw/refs/heads/master/2_04_wrangling/data/life_expectancy.csv",
destfile = "life-expectancy.csv")2 Get setup with Microsoft Copilot
Open a browser and navigate to Microsoft Copilot. Log in with your OSU credentials and indicate you are using your Work account

This would be the way to use generative AI that is compliant with with OSU’s data policies. You can learn more about this in OSU”s administrative resource center page on Copilot chat.
3 Get setup with chattr and ellmer
The package chattr is a chat interface to using a large language model (LLM) with R. chattr lets you “chat” with your LLM via your script or in a Shiny Gadget.
The package ellmer helps make it easier to use LLMs with R.
3.1 Install
First we will install both packages
install.packages("chattr")
install.packages("ellmer")Then we need to tell chattr which LLM we want to use. ellmer helps us do this, and at the time of writing this tutorial, it supports lots of different models:
- Anthropic’s Claude:
chat_anthropic() - AWS Bedrock:
chat_aws_bedrock() - Azure OpenAI:
chat_azure_openai() - Cloudflare:
chat_cloudflare() - Databricks:
chat_databricks() - DeepSeek:
chat_deepseek() - GitHub model marketplace:
chat_github(). - Google Gemini/Vertex AI:
chat_google_gemini(),chat_google_vertex(). - Groq:
chat_groq() - Hugging Face:
chat_huggingface() - Mistral:
chat_mistral() - Ollama:
chat_ollama() - OpenAI:
chat_openai() - OpenRouter:
chat_openrouter() - perplexity.ai:
chat_perplexity() - Snowflake Cortex:
chat_snowflake()andchat_cortex_analyst()` - VLLM:
chat_vllm()
You can pick which one you’d like to use, for the rest of this session I am going to use Google Gemini since I have a google/gmail account (as assume many of you do too), and their free tier is generous. I am including instructions on how to get your Google Gemini API key, but if you want to use a different model you can search how to find that API key.
Remember, your API key is personal so do not share it in repositories or elsewhere.
3.2 Set up your API key
To get your Google API key, go to https://aistudio.google.com/app/api-keys and sign in with your Google credentials.
I’m showing a screenshot below of what my Google AI studio looks like, yours may be slightly different and you want to create an API key if you don’t have one.
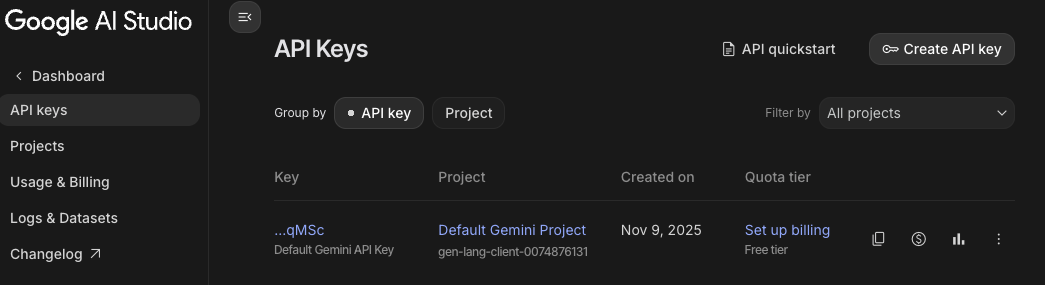
Then, you can click on the little double box to copy your API code. Your key code will be in your clipboard.
Now let’s set our API key. We can do that in R like this:
# for Gemini
Sys.setenv(GOOGLE_API_KEY = "YOUR_GOOGLE_API_KEY")Again - if you have this in your scripts be sure then not to share them with anyone.
There is a more elegant way to do this by setting up our API key in our R environment .Renviron file but I’m not going to set that up until we decide we like this :)
3.3 Use chattr
Now we are set up to launch our chat. First we need to load our packages.
library(chattr)
library(ellmer)Then we will tell chattr which LLM we want to use, with ellmer helping us:
chattr_use(ellmer::chat_google_gemini())Using model = "gemini-2.5-flash".
── chattr
• Provider: Google/Gemini
• Model: gemini-2.5-flash
• Label: gemini-2.5-flash (Google/Gemini)Let’s see how well that worked:
# check our settings
chattr_defaults()── chattr ──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── Defaults for: Default ──── Prompt: ── Model • Provider: Google/Gemini• Model: gemini-2.5-flash• Label: gemini-2.5-flash (Google/Gemini)── Context: Max Data Files: 0Max Data Frames: 0✖ Chat History✖ Document contentsNow we can launch our chat app.
chattr_app()4 Let’s ideate together what guidance we want to provide our LLM for helping us with code.
5 Tasks to play around with
Let’s together work on writing prompts to get R to write to complete each tasks or that answer the following questions:
Get R to read in your happiness and life expectancy data
Understand what your data contains
Which is the country with the highest life expectancy in 2025?
Which country increased life expectancy the most from 2000 to 2025?
Create a plot that shows the line expectancy in the United States over the time period for which we have data
Create a plot that shows the relationship between life expectancy and happiness score in 2022.